
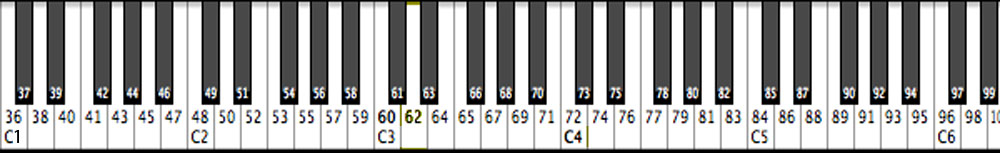
To note converter written by Andrew Botros. to the nearest note and how far it is out of tune, go to the frequency This table is reproduced below but inverted, i.e. to the nearest note and how far it is out of tune), go These data were used to calculate the first table below, which gives the frequency of any standard keyboard note By convention, A4 is often set at 440 Hz. Each semitone therefore has a ratio of 2 1/12 (approximately 1.059). See Frequency and Pitch for more details and an introduction to frequency and pitch.Īn octave is a ratio of 2:1 and, in equal temperament, an octave comprises 12 equal semitones. The musical interval between two notes depends on the ratio of their frequencies. The undefined CC’s you can map yourself to any assignable parameter on your synthesizer/instrument plugin.Note names, MIDI numbers and frequencies are related here in tables and via an application that converts them. 83 General Purpose Button 4 (on/off) Roland Tone level 4.82 General Purpose Button 3 (on/off) Roland Tone level 3.81 Hi Pass Filter Frequency or General Purpose Button 2 (on/off) Roland Tone level 2.80 Decay or General Purpose Button 1 (on/off) Roland Tone level 1.Sometimes you can assign them (and other CC mappings) yourself in the software instrument you use. NOTE: There is no standard CC value for Vibrato Amount or Vibrato Speed. However, some parameters are (on/off), where 0 to 63 = Off, 64 to 127 = On. They can truly add “life” to your music compositions, and even make orchestral music on software instruments feel expressive, organic and full of life! =)ĬC values have a range from 0-127, from minimum to maximum value. MIDI CC parameters are incredibly important for automation in your DAW to add movement, expression, variation etc. Hello Composers, Mike here, and I want to share a quick guide of the most common MIDI CC parameters.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
